Staff Selection Commission will hold an open competitive examination for recruitment to the posts of Junior Engineer
(Civil, Mechanical & Electrical) for Organizations/Offices of the Government
of India. The posts are of Group ‘B’ (Non-Gazetted), Non-Ministerial in Level-6 (Rs 35400-112400/-) of pay matrix of 7th Central Pay Commission. https://ssc.nic.in/
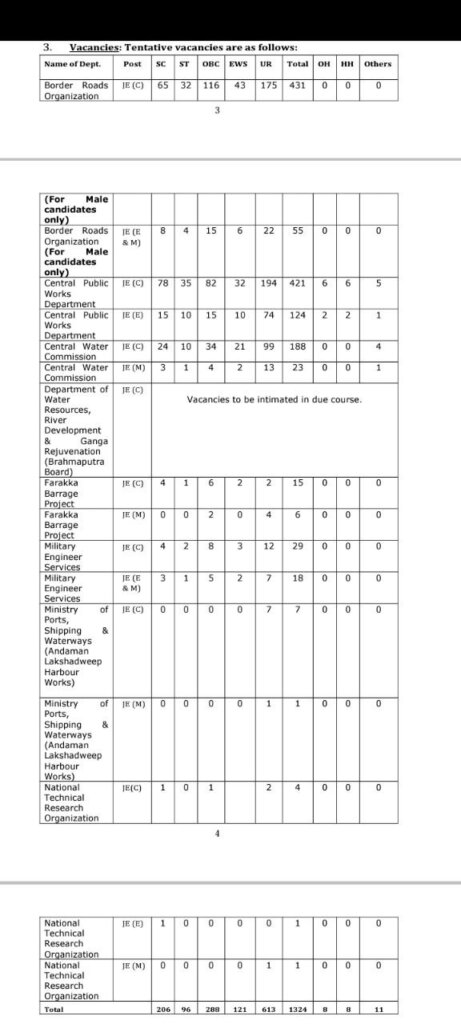
SSC JE 2023 VACANCY
Tentative vacancies are as follows:
SSC JE 2023 NEGETIVE MARKING
After 2022 now in ssc je negetive marking 1/3 . Questions in both papers will be of Objective Multiple Choice Type. Questions will be set in Hindi and English in Parts-I, II and III of Paper-I and Paper-II. There will be negative marking equal to one-third of the marks allotted to the question for each wrong answer in Paper-I & Paper-II. Candidates are, therefore, advised to keep this in mind while answering the questions.
Download SSC JE Previous year paper
SSC JE 2023 PAPER – 1 SYLLABUS
General Engineering: Civil & Structural, Electrical and Mechanical:
Part-A (Civil Engineering):
Building Materials, Estimating, Costing and Valuation, Surveying, Soil Mechanics, Hydraulics, Irrigation Engineering, Transportation Engineering, Environmental Engineering. Structural Engineering: Theory of Structures, Concrete Technology, RCC Design, Steel Design.
Part-B (Electrical Engineering):
Basic concepts, Circuit law, Magnetic Circuit, AC Fundamentals, Measurement and Measuring instruments, Electrical Machines, Fractional Kilowatt Motors and single phase induction Motors, Synchronous Machines, Generation, Transmission and Distribution, Estimation and Costing, Utilization and Electrical Energy, Basic Electronics.
Part-C Mechanical Engineering):
Theory of Machines and Machine Design, Engineering Mechanics and Strength of Materials, Properties of Pure Substances, 1st Law of Thermodynamics, 2nd Law of Thermodynamics, Air standard Cycles for IC Engines, IC Engine
Performance, IC Engines Combustion, IC Engine Cooling & Lubrication, Rankine cycle of System, Boilers, Classification, Specification, Fitting & Accessories, Air Compressors & their cycles, Refrigeration cycles, Principle of Refrigeration Plant, Nozzles & Steam Turbines. Properties & Classification of Fluids, Fluid Statics, Measurement of Fluid Pressure, Fluid kinematics, Dynamics of Ideal fluids, Measurement of Flow rate, basic principles, Hydraulic Turbines, Centrifugal Pumps, Classification of steel
SSC JE 2023 PAPER – 2 SYLLABUS
Part-A (Civil & Structural Engineering):
Building Materials: Physical and Chemical properties, classification, standard tests, uses and manufacture/quarrying of materials e.g. building stones, silicate based materials, cement (Portland), asbestos products, timber and wood based products, laminates, bituminous materials, paints, varnishes. Estimating, Costing and Valuation: estimate, glossary of technical terms, analysis of rates, methods and unit of measurement, Items of work earthwork, Brick work (Modular & Traditional bricks), RCC work, Shuttering, Timber work, Painting, Flooring, Plastering, Boundary wall, Brick building, Water Tank, Septic tank, Bar bending schedule, Centre line method, Mid-section formula, Trapezodial formula, Simpson’s rule, Cost estimate of Septic tank, flexible pavements, Tube well, isolates and combined footings, Steel Truss, Piles and pile-caps. Valuation – Value and cost, scrap value, salvage value, assessed value, sinking fund, depreciation and obsolescence, methods of valuation.
Surveying: Principles of surveying, measurement of distance, chain surveying, working of prismatic compass, compass traversing, bearings, local attraction, plane table surveying, theodolite traversing, adjustment of theodolite, Levelling, Definition of terms used in levelling, contouring, curvature and refraction corrections, temporary and permanent
adjustments of dumpy level, methods of contouring, uses of contour map, tachometric survey, curve setting, earth work calculation, advanced surveying equipment
Soil Mechanics: Origin of soil, phase diagram, Definitions-void ratio, porosity, degree of saturation, water content, specific gravity of soil grains, unit weights, density index and interrelationship of different parameters, Grain size distribution curves and their uses Index properties of soils, Atterberg‟s limits, ISI soil classification and plasticity chart
Permeability of soil, coefficient of permeability, determination of coefficient of permeability, Unconfined and confined aquifers, effective stress, quick sand, consolidation of soils, Principles of consolidation, degree of consolidation, pre-consolidation pressure, normally consolidated soil, elog p curve, computation of ultimate settlement Shear strength of soils, direct shear test, Vane shear test, Triaxial test Soil compaction, Laboratory compaction test, Maximum dry density and optimum moisture content, earth pressure theories, active and passive earth pressures, Bearing capacity of soils, plate load test, standard penetration test.
Hydraulics: Fluid properties, hydrostatics, measurements of flow, Bernoulli’s theorem and its application, flow through pipes, flow in open channels, weirs, flumes, spillways, pumps and turbines.
Irrigation Engineering: Definition, necessity, benefits, 2II effects irrigation, types and methods of irrigation, Hydrology – Measurement of rainfall, run off coefficient, rain gauge, losses from precipitation – evaporation, infiltration, etc Water requirement of crops, duty, delta and base period, Kharif and Rabi Crops, Command area, Time factor, Crop ratio, Overlap allowance, Irrigation efficiencies Different type of canals, types of canal irrigation, loss of water in canals Canal lining – types and advantages Shallow and deep to wells, yield from a well Weir and barrage, Failure of weirs and permeable foundation, Slit and Scour, Kennedy’s theory of critical velocity Lacey’s theory of uniform flow Definition of flood, causes and effects, methods of flood control, water logging, preventive measure Land reclamation, Characteristics of affecting fertility of soils, purposes, methods, description of land and reclamation processes Major irrigation projects in India
Transportation Engineering: Highway Engineering – cross sectional elements, geometric design, types of pavements, pavement materials – aggregates and bitumen, different tests, Design of flexible and rigid pavements – Water Bound Macadam (WBM) and Wet Mix Macadam (WMM), Gravel Road, Bituminous construction, Rigid pavement joint,
pavement maintenance, Highway drainage, Railway Engineering Components of permanent way – sleepers, ballast, fixtures and fastening, track geometry, points and crossings, track junction, stations and yards Traffic Engineering – Different traffic survey, speed-flow-density and their interrelationships, intersections and interchanges, traffic signals, traffic operation, traffic signs and markings, road safety.
Environmental Engineering: Quality of water, source of water supply, purification of water, distribution of water, need of sanitation, sewerage systems, circular sewer, oval sewer, sewer appurtenances, sewage treatments Surface water drainage Solid waste management – types, effects, engineered management system Air pollution – pollutants, causes, effects, control Noise pollution – cause, health effects, control
Structural Engineering: Theory of structures: Elasticity constants, types of beams – determinate and indeterminate, bending moment and shear force diagrams of simply supported, cantilever and over hanging beams Moment of area and
moment of inertia for rectangular & circular sections, bending moment and shear stress for tee, channel and compound sections, chimneys, dams and retaining walls, eccentric loads, slope deflection of simply supported and cantilever beams, critical load and columns, Torsion of circular section.
Concrete Technology: Properties, Advantages and uses of concrete, cement aggregates, importance of water quality, water cement ratio, workability, mix design, storage, batching, mixing, placement, compaction, finishing and curing of concrete, quality control of concrete, hot weather and cold weather concreting, repair and maintenance of concrete structures
RCC Design: RCC beams-flexural strength, shear strength, bond strength, design of singly reinforced and double reinforced beams cantilever beams T-beams, lintels One way and two way slabs, isolated footings Reinforced brick works, columns, staircases, retaining wall, water tanks (RCC design questions may be based on both Limit State and Working Stress methods)
Steel Design: Steel design and construction of steel columns, beams roof trusses plate girders
Is there 1/3 NEGETIVE MARKING IN SSC JE ?
Yes that time 1/3 negetive in SSC JE